Our Editors-in-Chief’s Top Picks
The Editors-in-Chief of our CASS publications have selected some noteworthy papers from the recent issues of our journals:
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs
Paper 1:
S. Abdelfattah, H. M. E. Hussein, A. Shrivastava and M. Onabajo, "Instrumentation Amplifier Input Impedance Calibration With Machine Learning-Based Optimizations," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 72, no. 2, pp. 394-398, Feb. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2025.3526145. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10829648
Summary: This work introduces a digital calibration technique to boost the input impedance of instrumentation amplifiers (IAs) with digitally tunable input impedance. The technique employs two machine learning-driven optimization algorithms, the genetic algorithm (GA) and the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm, to efficiently control integrated capacitor banks within the IA for the determination of the optimal input impedance. A prototype platform was developed to automatically optimize a fabricated IA test chip designed with 65-nm CMOS technology, which allows to test the machine learning algorithms using a microcontroller to control the digitally tunable input impedance. With an extra input capacitance of 100 pF, the GA algorithm achieved an input impedance of 1.75 GΩ after four generations (iterations), while the PSO algorithm achieved 1.27 GΩ with five iterations.
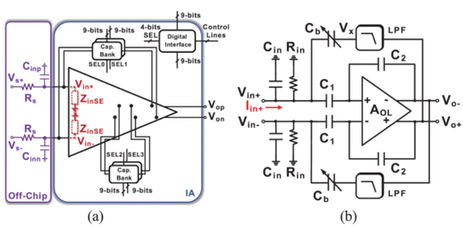
Paper 2:
D. Basak, S. Huang and G. Yuan, "On the Effect of Memory Error in a Time-Interleaved Pipeline ADC With a Shared Residue Amplifier," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 72, no. 3, pp. 434-438, March 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2025.3526875
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10833849
Summary: This brief analyzes the effect of memory error and presents a simple digital memory correction technique for a reset-free and shared open-loop-based pipeline ADC. A 14-bit TI pipeline-SAR ADC, running at 2 GS/s, is designed and fabricated to verify the proposed analysis and correction method. Experimental results show improvements of up to 5.1 dB in the signal-to-noise-and-distortion ratio (SNDR) and more than two times in the integral nonlinearity (INL) with the proposed digital memory correction technique.
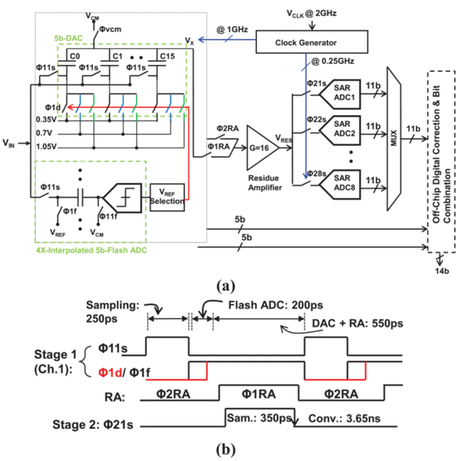
Paper 3:
T. Zhao and G. A. Rincón-Mora, "Unraveling Negative Feedback Translations: Gains, Peaking, Stability, and Loop Variations," in IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, vol. 72, no. 3, pp. 454-458, March 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2025.3531242. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10844875
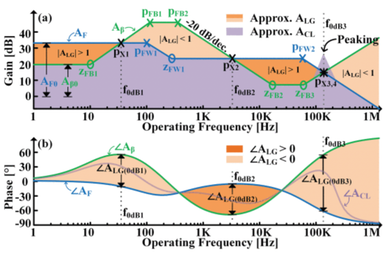
Summary: This brief develops a quick, precise, and insightful method for analyzing the closed-loop frequency response, peaking, and stability of complex negative feedback systems. Loop variations are explored to simplify analysis for complex feedback loops. The proposed method improves on the state-of-the-art by emphasizing circuit intuition, reducing algebraic complexity, simplifying complex feedback loops, while preserving the accuracy of the exact solution. The result shows that the closed-loop response follows the lowest forward translation across frequencies, verified by SPICE and MATLAB simulations.
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technologies
Paper 1:
H. Amirpour, M. Ghanbari and C. Timmerer, "DeepStream: Video Streaming Enhancements Using Compressed Deep Neural Networks," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 3786-3797, April 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3229079 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9984695
Summary: This paper proposes a scalable content-aware per-title encoding approach, called DeepStream, to support both CPU-only and GPU-available end-users. To support backward compatibility, DeepStream constructs a bitrate ladder based on any existing per-title encoding approach. Therefore, the video content is provided for legacy end-user devices with CPU-only capabilities as a base layer (BL). For high-end end-user devices with GPU capabilities, an enhancement layer (EL) is added on top of the base layer comprising lightweight video super-resolution deep neural networks (DNNs) for each bitrate-resolution pair of the bitrate ladder. A content-aware video super-resolution approach leads to higher video quality, at the cost of bitrate overhead. To reduce the bitrate overhead for streaming content-aware video super-resolution DNNs, DeepCABAC, context-adaptive binary arithmetic coding for DNN compression, is used. Furthermore, the similarity among segments within a scene and frames within a segment are used to reduce the training costs of DNNs. Experimental results show bitrate savings of 34% and 36% to maintain the same PSNR and VMAF, respectively, for GPU-available end-users, while the CPU-only users get the desired video content as usual.
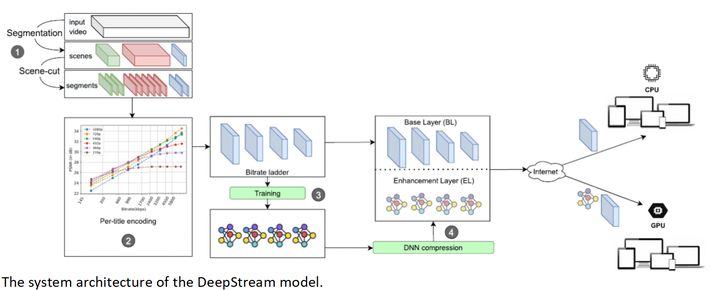
Paper 2:
K. Fischer, F. Brand and A. Kaup, "Boosting Neural Image Compression for Machines Using Latent Space Masking," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 3719-3731, April 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.319532 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9845478
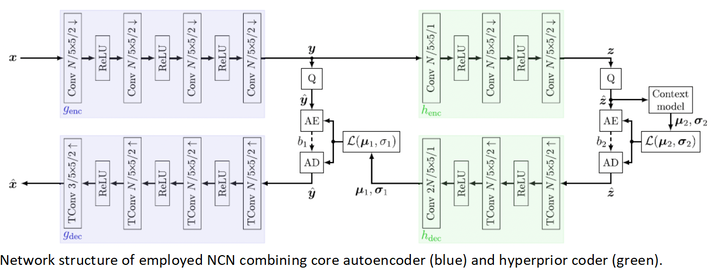
Summary: This paper presents several methods to enhance the compression performance of Neural Compression Networks (NCNs) when coding for a neural network as information sink by sacrificing visual quality. As a main contribution, this paper proposes a network, called LSMnet, that runs in parallel to an encoder network and masks out elements of the latent space that are presumably not required for the analysis network. By this approach, additional 27.3% of bitrate are saved compared to the basic neural compression network optimized with the task loss. A feature-based distortion is also utilized in the training loss within the context of machine-to-machine communication, which allows for a training without annotated data. Analyses is reported on the Cityscapes dataset including cross-evaluation with different analysis networks and exemplary visual results are also shown..
Paper 3:
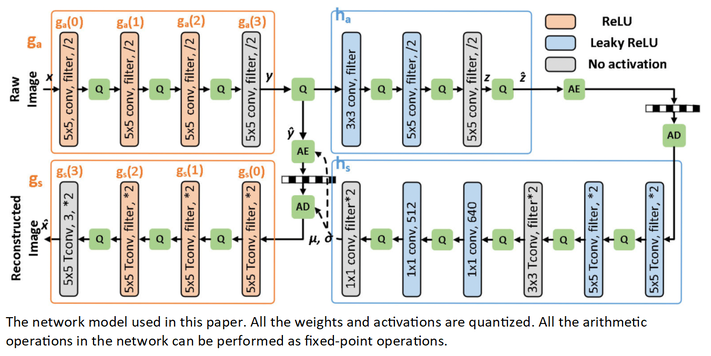
H. Sun, L. Yu and J. Katto, "Q-LIC: Quantizing Learned Image Compression With Channel Splitting," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 3798-3811, April 2025, doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3231789 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9997555
Summary: This paper presents a Quantized Learned Image Compression (QLIC) by channel splitting. First, it is explored that the influence of the quantization error to the reconstruction error is different for various channels. Second, the channels are split whose quantization has larger influence to the reconstruction error. After the splitting, the dynamic range of channels is reduced so that the quantization error can be reduced. Finally, several channels are pruned to keep the number of overall channels as origin. By using the proposal, in the case of 8-bit quantization for weight and activation of both main and hyper path, the BD-rate is reduced by 0.61%-4.74% compared with the previous QLIC. Better coding gain can be reached compared with the state-of-the-art network quantization method when quantizing MS-SSIM models. This proposed solution can be also combined with other network quantization methods to further improve the coding gain. The moderate coding loss caused by the quantization validates the feasibility of the hardware implementation for QLIC in the future.
IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems
Paper 1:
Das, S., Riedel, S., Naeim, M., Brunion, M., Bertuletti, M., Benini, L., Ryckaert, J., Myers, J., Biswas, D. and Milojevic, D., 2024. "Bandwidth-Latency-Thermal Co-Optimization of Interconnect-Dominated Many-Core 3D-IC," IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems. vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 346-357, Feb. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2024.3467148 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10720515
Summary: The article addresses the challenges faced by contemporary system-on-chips (SoCs) due to the increasing demands for memory bandwidth, capacity, and thermal stability, particularly in the context of advancing artificial intelligence (AI). It proposes architectural modifications for a many-core SoC designed to enhance on-chip cache memory bandwidth and optimize access latency. The SoC is fabricated using A10 nanosheet technology in a 3-D configuration, with thermal analyses conducted. Workload simulations demonstrate significant performance improvements, achieving up to 12-fold acceleration for a 64-core version and 2.5-fold for a 16-core version, accompanied by a 40% increase in die area and a 60% rise in power dissipation when using a 2-D design. In comparison, the 3-D design not only minimizes the physical footprint but also saves 20% in power consumption due to a 40% reduction in wirelength. The study emphasizes the importance of restructuring pipelines to optimize the benefits of 3-D technology for enhanced memory access and lower latency. Additionally, it explores thermal impacts of different 3-D partitioning approaches in high-performance computing (HPC) and mobile applications, finding that 3-D designs in mobile contexts only slightly increase maximum temperature (by about 2-3 °C) compared to 2-D, while HPC scenarios require careful partitioning strategies to effectively manage thermal constraints.
Paper 2:
G. Murali, M. Gyu Park and S. Kyu Lim, "3DNN-Xplorer: A Machine Learning Framework for Design Space Exploration of Heterogeneous 3-D DNN Accelerators," IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 358-370, Feb. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2024.3471496. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10715720
Summary: This paper introduces 3DNN-Xplorer, a novel machine learning (ML)-based framework for predicting the performance of heterogeneous 3-D deep neural network (DNN) accelerators. This framework enables design space exploration (DSE) of these accelerators with a two-tier compute-on-memory (CoM) configuration, considering 3-D physical design factors. The framework explores four distinct heterogeneous 3-D integration styles combining 28-nm and 16-nm technology nodes for both compute and memory tiers. Through extrapolation techniques and ML models trained on various accelerator configurations, the performance of larger systems is estimated, achieving a maximum absolute error of 13.9%. The framework considers area imbalance arising from different technology nodes by assuming equal numbers of PEs or on-chip memory capacity across integration styles. The analysis reveals that the heterogeneous 3-D style with 28-nm compute and 16-nm memory demonstrates energy-efficient performance, offering up to 50% energy savings and an 8.8% reduction in runtime compared to other 3-D integration styles. Conversely, the heterogeneous 3-D style with 16-nm compute and 28-nm memory proves area-efficient, exhibiting up to 8.3% runtime reduction compared to other 3-D styles.
Paper 3:
A. Almeida da Silva, L. Nogueira, A. Coelho, J. A. N. Silveira and C. Marcon, "Securet3d: An Adaptive, Secure, and Fault-Tolerant Aware Routing Algorithm for Vertically–Partially Connected 3D-NoC," IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 275-287, Jan. 2025, doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2024.3500575 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10766899
Summary: This article presents Securet3d, a novel routing algorithm designed for multiprocessor systems-on-chip (MPSoCs) that utilize 3-D networks-on-chip (3D-NoCs), aimed at enhancing secure and fault-tolerant operations. As MPSoCs play a crucial role in achieving effective parallel computing by sharing resources across complex applications, implementing adaptive mechanisms to safeguard sensitive data is essential. Securet3d builds upon the existing Reflect3d algorithm, introducing a comprehensive mapping scheme for secure data pathways and improving the system’s fault tolerance. The algorithm's effectiveness is validated through comparisons with three other fault-tolerant routing algorithms in vertically-partially connected 3D-NoCs. All algorithms were developed in SystemVerilog and evaluated via simulations using ModelSim, and hardware synthesis was performed with Cadence’s Genus tool. The experimental results indicate that Securet3d not only reduces latency but also enhances cost-effectiveness compared to other methods. Implemented with a 28-nm technology library, Securet3d exhibits minimal area and energy overhead, demonstrating its scalability and efficiency. Moreover, during denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, Securet3d maintains relatively stable average packet latencies of 70, 90, and 29 clock cycles for uniform random, bit-complement, and shuffle traffic, respectively, which are significantly lower than the latencies observed in other algorithms lacking security mechanisms (5763, 4632, and 3712 clock cycles on average). These findings underscore Securet3d's superior security, scalability, and adaptability for complex communication systems.
IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems
Paper 1:
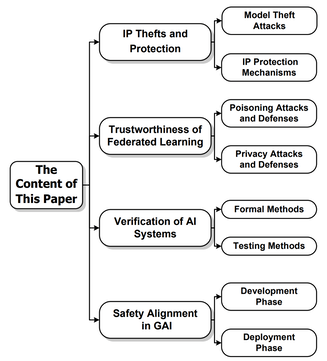
Y. Zheng, C. -H. Chang, S. -H. Huang, P. -Y. Chen and S. Picek, "An Overview of Trustworthy AI: Advances in IP Protection, Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning, Security Verification, and GAI Safety Alignment," IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 582-607, Dec. 2024, doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2024.3477348. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10711270
Summary: This overview paper anchors on recent advances in four research hotspots of trustworthy AI with compelling and challenging security, privacy, and safety issues. The topics discussed include the intellectual property protection of deep learning and generative models, the trustworthiness of federated learning, verification and testing tools of AI systems, and the safety alignment of generative AI systems. Discussions regarding the challenges and opportunities associated with each topic are also presented, with the hope of inspiring potential research directions and steering technological advancement toward the development of beneficial AI.
Paper 2:
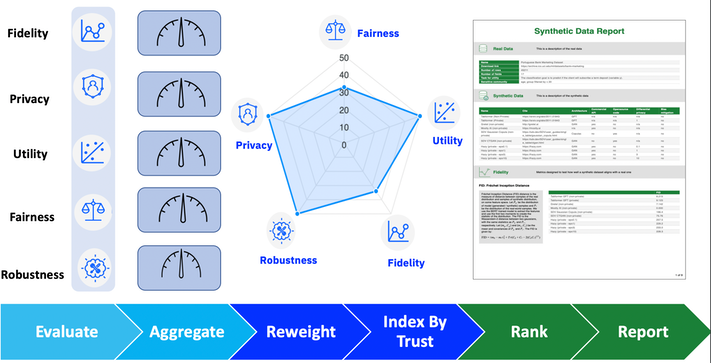
B. Belgodere et al., "Auditing and Generating Synthetic Data With Controllable Trust Trade-Offs," in IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 773-788, Dec. 2024, doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2024.3477976. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10713321
Summary: Synthetic datasets help tackle critical challenges like biases, imbalances, and privacy risks in real-world data, but ensuring their trustworthiness remains a significant hurdle. To address this, we propose a comprehensive auditing framework that evaluates generative AI models and synthetic datasets across tabular, time-series, vision, and natural language data for bias prevention, fidelity, privacy preservation, and utility. Our auditing framework provides clear, transparent reports via communicating trustworthiness indices, that ensure trust and compliance in synthetic data generation.
Paper 3:
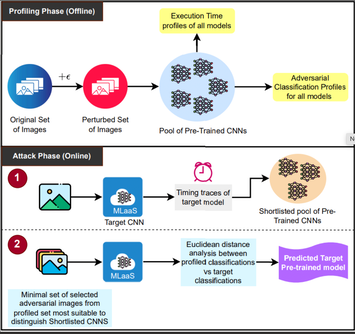
S. Shukla, M. Alam, P. Mitra and D. Mukhopadhyay, "Stealing the Invisible: Unveiling Pre-Trained CNN Models Through Adversarial Examples and Timing Side-Channels," IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 634-646, Dec. 2024, doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2024.3485133. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10731906
Summary: Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS) platforms increasingly rely on pre-trained models, making it vital to safeguard architectures and address their vulnerabilities. We introduce ArchWhisperer, a novel model fingerprinting attack that exploits adversarial image misclassifications and inference time profiling to efficiently steal CNN and Vision Transformer architectures. Our approach achieves 88.8% accuracy across 27 pre-trained models on CIFAR-10 while keeping the query budget below 20, significantly outperforming prior works.
IEEE Open Journal of Circuits and Systems
Paper 1:
T. Kaiser, E. Gottschalk, K. Biethahn and F. Gerfers, "Pasithea-1: An Energy-Efficient Sequential Reconfigurable Array With CPU-Like Programmability," IEEE Open Journal of Circuits and Systems, vol. 6, pp. 1-13, 2025, doi: 10.1109/OJCAS.2024.3518110. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10802954
Summary: This work presents Pasithea-1, a coarse-grained reconfigurable array (CGRA) that combines energy efficiency with CPU-like programmability.
Paper 2:
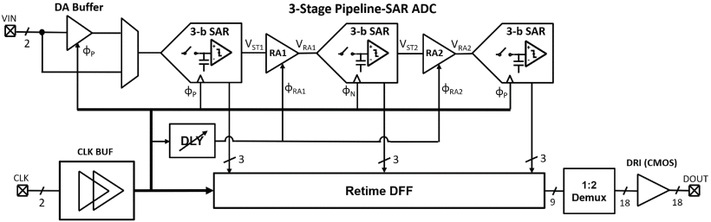
B. Yang, T. Caldwell and A. Chan Carusone, "An Energy-Efficient Pipeline-SAR ADC Using Linearized Dynamic Amplifiers and Input Buffer in 22nm FDSOI," IEEE Open Journal of Circuits and Systems, vol. 6, pp. 50-62, 2025, doi: 10.1109/OJCAS.2024.3509746. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10774063
Summary: This work presents a dynamic amplifier that achieves −52 dB in total harmonic distortion through an analog technique by which the expanding and compressing nonlinearities in the input transistors cancel one another. A pipeline-SAR analog-to-digital converter incorporating the linearized dynamic amplifier in both the input buffer and the first residue amplifier stage was designed and fabricated using the GlobalFoundries 22nm fully depleted silicon-on-insulator process.
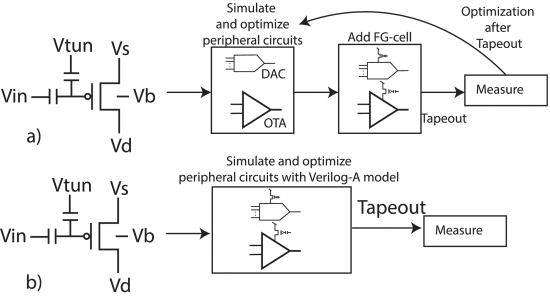
Paper 3:
S. Nowshin Chowdhury, M. Chen and S. Shah, "Analysis and Verilog-A Modeling of Floating-Gate Transistors," IEEE Open Journal of Circuits and Systems, vol. 6, pp. 63-73, 2025, doi: 10.1109/OJCAS.2024.3524363. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10818976
Summary: This work presents a Verilog-A model based on empirical measurements for a floating-gate transistor fabricated using a 65 nm CMOS process.
________________
IEEE CAS Magazine First Quarter Issue 2025

IEEE Circuits and Systems (CAS) Magazine publishes original review articles and other articles that are of broad interest to the Circuits and Systems Society community. Interested authors are invited to send a three to four page White Paper first to the Editor-in-Chief, Prof. Keshab K. Parhi, by email here. If invited, they can submit a Full Paper at the Author Portal at the link below. CAS Magazine will continue to publish articles related to CAS Society Outreach. In addition, CAS Magazine also publishes articles related to education (such as tricks in solving problems and short lecture notes), conference highlights, chapter highlights, applications, and standards. Please feel free to submit articles that are of broad interest to the members of the CAS Society. For more information, please visit the IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine on the CASS website.
Table of Contents
Beginning of a New Year and a New Quarter Century [Editorial]
Keshab K. Parhi
75th Anniversary of the IEEE CAS Society [President’s Message]
Myung Hoon Sunwoo
Secure Machine Learning Hardware: Challenges and Progress [Feature]
Kyungmi Lee; Maitreyi Ashok; Saurav Maji; Rashmi Agrawal; Ajay Joshi; Mengjia Yan; Joel S. Emer; Anantha P. Chandrakasan
A Survey: Collaborative Hardware and Software Design in the Era of Large Language Models
Cong Guo; Feng Cheng; Zhixu Du; James Kiessling; Jonathan Ku; Shiyu Li; Ziru Li; Mingyuan Ma; Tergel Molom-Ochir; Benjamin Morris; Haoxuan Shan; Jingwei Sun; Yitu Wang; Chiyue Wei; Xueying Wu; Yuhao Wu; Hao Frank Yang; Jingyang Zhang; Junyao Zhang; Qilin Zheng; Guanglei Zhou; Hai Li; Yiran Chen
Linearity Through Democracy [Feature]
Enrique Alvarez-Fontecilla; Paul S. Wilkins
Celebrating 15 Years of IEEE Latin American Symposium on Circuits and Systems (LASCAS) [CASS Regional Conference Celebration]
Francois Rivet; Carlos Silva-Cardenas; Fernando Silveira; Victor Grimblatt; Ricardo Reis
Creating a Sustainable Future Workshop: Cultivating a Green and Resilient Environment in CAS and Reliability for Security in Hardware [CASS Regional Outreach]
Yi Wang; Kea-Tiong Tang
Webinar for IEEE CASS YPCAS by Prof. Zhicong Huang [CASS Young Professionals Corner]
Chi-Seng Lam
IEEE Young Professionals in Circuits and Systems (YPCAS) Forum 2024 at University of Macau, Macau SAR, China [CASS Young Professionals Corner]
Chi-Seng Lam
IEEE Standards Workshop on AI for Healthcare [Standards Corner]
Yongfu Li; Jiajun Yuan; Yang Zhao; Liebin Zhao; Yong Lian
Empowering Open Innovation Through IEEE CAS Society Conferences’ Grand Challenges and the Development of Robust IEEE Standards [Open Innovations and Standards]
Yongfu Li; Yin Yong; Guoxing Wang; Liebin Zhao; Yong Lian
CASS Tainan Chapter Hosts Distinguished Lecturer Gabriel A. Rincon-Mora [CASS Chapter Highlights]
Cheng-Ta Chiang
________________
Active "Call for Papers” Archive
______________________________
Latest Tables of Contents of CAS Sponsored Journals
The latest issues of our CAS sponored journals have been published and the tables of contents can be accessed through the following links:

- IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers
- IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs
- IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology
- IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems
- IEEE Circuits and Systems Magazine
- IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems
- IEEE Design and Test Magaz

